How to check the financing margin rate and margin margin rate of a stock?
Click the yellow “Financing” icon in the upper right corner of the stock chart page, and the system will pop up a prompt box to explain whether the stock supports margin or securities lending, as well as the relevant margin ratio, reference interest rate, etc.
Special Instructions:
- Due to liquidity, risk control or regulatory reasons, some stocks may not be allowed to short sell securities for the time being, even if they support financing long.
- If you see “Short Selling Pool Remaining = 0”, it means that there is no available margin for securities borrowing and borrowing at the moment, but the stock itself supports short selling.
- If the initial margin is 100%, or if ‘–’ is prompted, it means that margin or securities lending is not supported
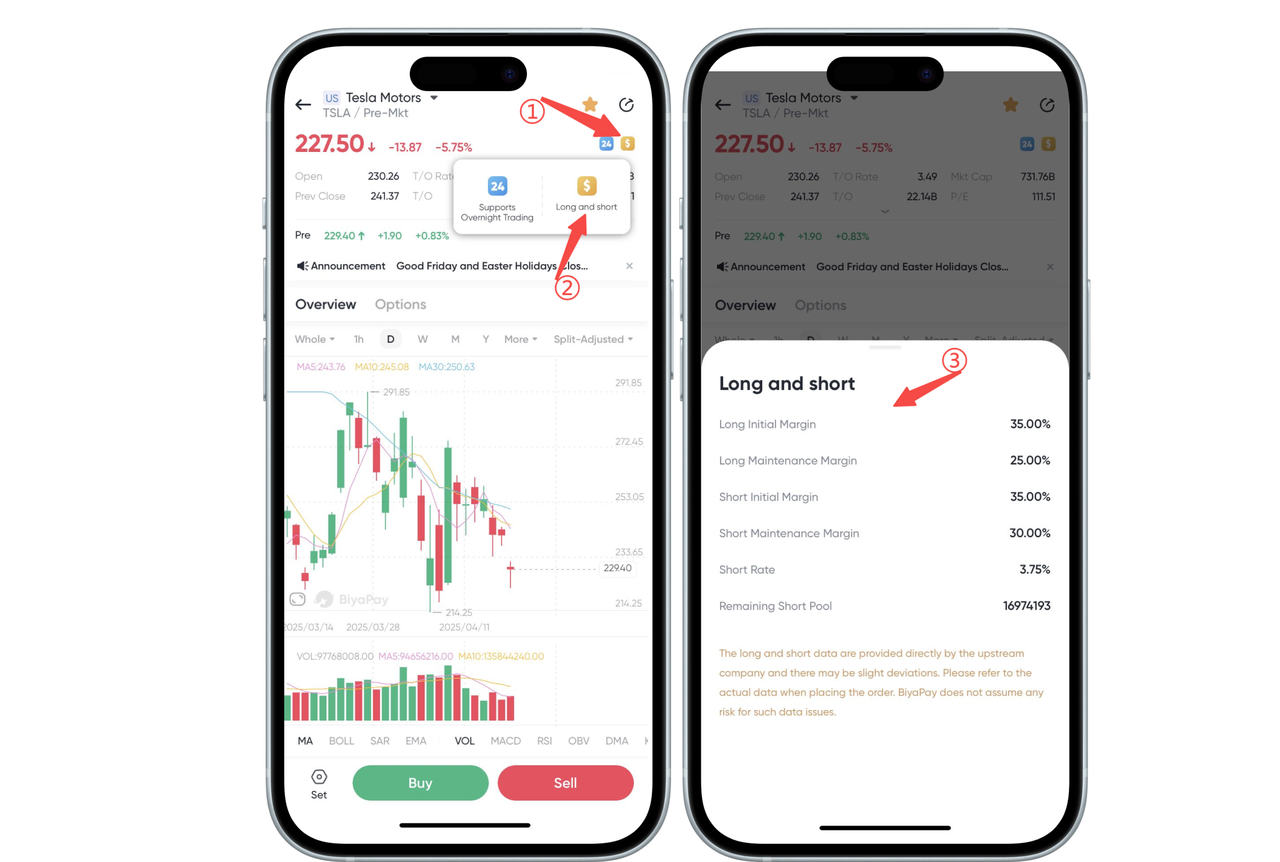
1.Initial Margin for Long Position
Definition: Long Initial Margin is the minimum amount that an investor must deposit into a margin account when opening a long positioning (i.e. buying a stock). This is usually part of the stock purchase price and is stipulated by the exchange or broker.
Example: If the exchange requires an initial margin of 50% and an investor wants to buy $10,000 worth of stock, they need to deposit $5,000 as an initial margin.
2.Maintenance Margin for Long Positions
Definition: Long Maintenance Margin refers to the minimum margin level that an investor must maintain in his account during the period of holding long positioning. If the account margin is lower than this level, the investor will receive a Margin Call (margin call) to deposit more funds or sell some shares.
Example: If the Maintenance Margin ratio is 30% and the investor’s stock market value drops to $8,000, they need to maintain a minimum margin of $2,400 (30% of $8,000). If the margin in the account is less than $2,400, the investor needs to make additional margin.
3.Initial Margin for Short Position
Definition: Short initial margin refers to the minimum amount that an investor must deposit into a margin account when opening a short positioning (i.e. selling a borrowed stock). This is to ensure that the investor has the ability to bear potential losses when the stock price rises.
Example: If the initial margin required by the exchange is 50% and an investor wants to sell short $10,000 worth of stock, they need to deposit $5,000 as the initial margin.
4.Maintenance Margin for Short Positions
Definition: Short Maintenance Margin refers to the minimum margin level that an investor must maintain in the account during the period of holding a short positioning. If the account margin falls below this level, the investor will receive a Margin Call.
Example: If the Maintenance Margin ratio is 30% and the investor sells short stock with a market value of $12,000, they need to maintain a margin of at least $3,600 (30% of $12,000). If the margin in the account is less than $3,600, the investor needs to make an additional margin.
5.Sell short interest rate
Definition: sell short reference rate is the interest rate that investors pay to stock lenders when they borrow stock to sell short. This is one of the costs of sell short transactions.
Example: If the sell short reference interest rate is 5%, and an investor borrows $10,000 worth of stock to sell short, they pay $500 in annual interest (5% of $10,000) to the lender.
6.Sell short Sale Pool Remaining
Definition: sell short pool surplus refers to the number of shares available for lending for sell short operations. This value will vary with market demand. If sell short demand is high, sell short pool surplus will decrease, and vice versa.
Example: If there are 50,000 shares remaining in the sell short pool of a stock, it means that there are currently 50,000 shares available for investors to borrow to sell short. This value decreases as more investors borrow to sell short.
By understanding these terms and their operation, you can better grasp the margin requirements and risk management in US and Hong Kong stock trading.
Contact Us
BIYA GLOBAL LLC is a licensed entity registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC No.: 802-127417); a certified member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (Central Registration Depository CRD No.: 325027); regulated by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
BIYA GLOBAL LLC is registered with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), an agency under the U.S. Department of the Treasury, as a Money Services Business (MSB), with registration number 31000218637349, and regulated by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
BIYA GLOBAL LIMITED is a registered Financial Service Provider (FSP) in New Zealand, with registration number FSP1007221, and is also a registered member of the Financial Services Complaints Limited (FSCL), an independent dispute resolution scheme in New Zealand.














