The Leading U.S. Banks in Life Insurance Asset Management

Image Source: unsplash
Bank of America, Wells Fargo, and JPMorgan Chase lead the list of banks ranked by life insurance assets in the United States. These assets play a vital role for the largest banks in the US.
- Recent research shows that life insurance assets help banks diversify income, improve customer loyalty, and reduce liquidity risks.
- Life insurance also supports bank stability by offering financial security for borrowers and strengthening income sources.
A ranking table and detailed analysis of banks ranked by life insurance assets appears in the following section.
Key Takeaways
- Bank of America, Wells Fargo, and JPMorgan Chase lead U.S. banks in life insurance assets, using these assets to strengthen financial stability and support growth.
- Life insurance assets help banks manage risk, provide steady income, and offer benefits to employees, making them a valuable part of bank portfolios.
- Banks use unique strategies like bancassurance and investment in long-term assets to compete with life insurance companies and improve returns.
- Regulators monitor life insurance assets closely to ensure banks remain strong during market changes and financial stress.
- Recent trends show more banks increasing life insurance holdings, highlighting its growing importance in banking and financial stability.
Banks Ranked by Life Insurance Assets

Image Source: pexels
Ranking Table
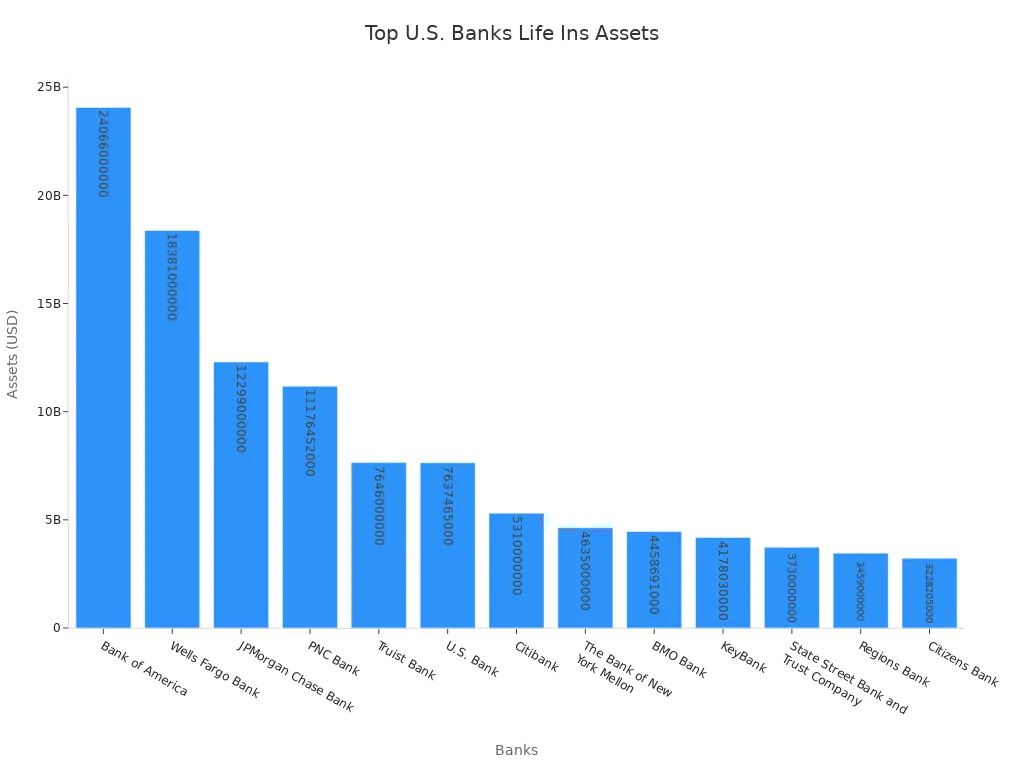
Banks ranked by life insurance assets show clear differences in their asset portfolios. The table below lists the top banks in the United States by the value of their life insurance assets. These numbers reflect the latest available data.
| Rank | Bank Name | Life Insurance Assets (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bank of America | $24,066,000,000 |
| 2 | Wells Fargo Bank | $18,381,000,000 |
| 3 | JPMorgan Chase Bank | $12,299,000,000 |
| 4 | PNC Bank | $11,176,452,000 |
| 5 | Truist Bank | $7,646,000,000 |
| 6 | U.S. Bank | $7,637,465,000 |
| 7 | Citibank | $5,310,000,000 |
| 8 | The Bank of New York Mellon | $4,635,000,000 |
| 9 | BMO Bank | $4,458,691,000 |
| 10 | KeyBank | $4,178,030,000 |
| 11 | State Street Bank and Trust Company | $3,730,000,000 |
| 12 | Regions Bank | $3,459,000,000 |
| 13 | Citizens Bank | $3,228,205,000 |
Banks ranked by life insurance assets often use these holdings to support their financial strength. Life insurance assets help banks manage risk and provide stable returns. Many banks also use life insurance to support employee benefit programs and to diversify their investment portfolios.
Top Three Banks
Bank of America holds the largest life insurance asset portfolio among U.S. banks. Its life insurance assets total over $24 billion. This amount puts Bank of America at the top of the list of banks ranked by life insurance assets. Wells Fargo Bank follows with more than $18 billion in life insurance assets. JPMorgan Chase Bank comes in third, holding over $12 billion in life insurance assets.
These three banks stand out for several reasons:
- Bank of America: This bank leads the group with the highest life insurance asset value. It uses life insurance to support its financial stability and to offer benefits to employees. Bank of America also has a large network, with over 3,600 branches and a strong focus on domestic assets.
- Wells Fargo Bank: Wells Fargo ranks second in life insurance assets. It manages almost all its assets in the United States. The bank uses life insurance to help manage risk and to provide long-term value for its customers and shareholders.
- JPMorgan Chase Bank: JPMorgan Chase holds the third spot. It has a large presence both in the United States and abroad. The bank uses life insurance assets to support its global operations and to strengthen its balance sheet.
Note: The top three banks have much larger life insurance asset portfolios than other banks on the list. This difference shows how important life insurance is for the largest banks in the country.
Banks ranked by life insurance assets often compete with life insurance companies for investment returns. The top life insurance companies also manage large portfolios, but banks use different strategies. Banks focus on using life insurance to support their core business and to provide extra security for their customers and employees.
Life insurance plays a key role in the banking sector. It helps banks manage risk, support growth, and compete with life insurance companies. The largest banks use life insurance assets to stay strong and to offer better services to their clients.
Life Insurance in U.S. Banking
Asset Significance
Life insurance plays a key role in the financial health of the largest banks in the us. These banks use life insurance to manage risk and support long-term growth. A life insurance policy can help banks protect their employees and provide benefits. Many banks invest in life insurance because it offers stable returns and helps balance their portfolios.
Bank-owned life insurance, or BOLI, is a common tool. Banks purchase life insurance policies on employees and use the cash value as an asset. This cash value grows over time and provides a steady source of income. Banks can use these funds to pay for employee benefits or other expenses. Life insurance assets also help banks meet Tier 1 capital requirements. Tier 1 capital is the core measure of a bank’s financial strength. By holding life insurance, banks can improve their capital ratios and show regulators they are stable.
Life insurance assets offer many coverage options. These options allow banks to choose the best fit for their needs. Some banks select coverage options that focus on high returns, while others prefer options that offer more security. The flexibility of coverage options makes life insurance a valuable asset for banks.
Regulatory Role
Regulators pay close attention to life insurance in banking. The Federal Reserve Board sets rules for capital requirements. These rules help ensure banks remain strong during tough times. The Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC) also monitors banks and insurance companies. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) works to modernize solvency standards.
Financial reports show that life insurance assets help banks stay stable. During the 2007-2009 financial crisis, life insurance companies showed strong performance. Their assets, such as investment-grade bonds, provided steady income. Life insurance companies faced less risk because they had long-term funding and fewer ties to other financial firms. Banks use similar strategies with life insurance assets to reduce risk and support growth.
Life insurance gives banks more coverage options for managing risk. These options help banks prepare for changes in the market. By using life insurance, banks can protect themselves and their customers.
What Sets the Largest Banks Apart
Strategies
Leading banks in life insurance asset management use several unique strategies to stay ahead. They focus on innovative investment methods to solve the challenge of earning good returns when interest rates are low. These banks manage the length of their investments carefully and keep most of their portfolios in investment-grade assets. They also look for new opportunities in non-traditional fixed-income sectors, such as structured credit. This approach helps them use the long-term nature of life insurance liabilities to take on more illiquidity risk, which can lead to better returns.
Banks often use bancassurance channels, where their subsidiaries sell life insurance products. This method allows banks to enter the market quickly and build cost-effective sales channels. Unlike traditional sales channels that depend only on the sales teams of life insurance companies, bancassurance lets banks reach more customers through their branch networks. Data envelopment analysis shows that bancassurance can be more efficient than traditional channels, especially when banks have many branches and sales representatives.
The largest life insurance companies usually rely on their own agents and focus on building strong brands. In contrast, banks use their wide customer base and branch networks to offer life insurance and different coverage options. This difference in strategy helps banks compete with the best life insurance company and other financial services corporations.
Market Position
The largest banks hold a strong position in the life insurance market. They use their size and resources to manage large portfolios and offer a wide range of coverage options. Their ability to cross-sell life insurance with other banking products gives them an edge over many life insurance companies.
Banks also benefit from their experience in managing risk and investments. They often outperform smaller banks and some life insurance companies by using advanced investment strategies. The largest life insurance companies still lead in product design and underwriting, but banks excel in distribution and customer reach.
Note: The combination of strong investment skills, large branch networks, and bancassurance channels helps banks stand out in life insurance asset management. Their strategies allow them to compete with both other banks and the largest life insurance companies, making them key players in the industry.
Trends and Changes

Image Source: unsplash
Recent Shifts
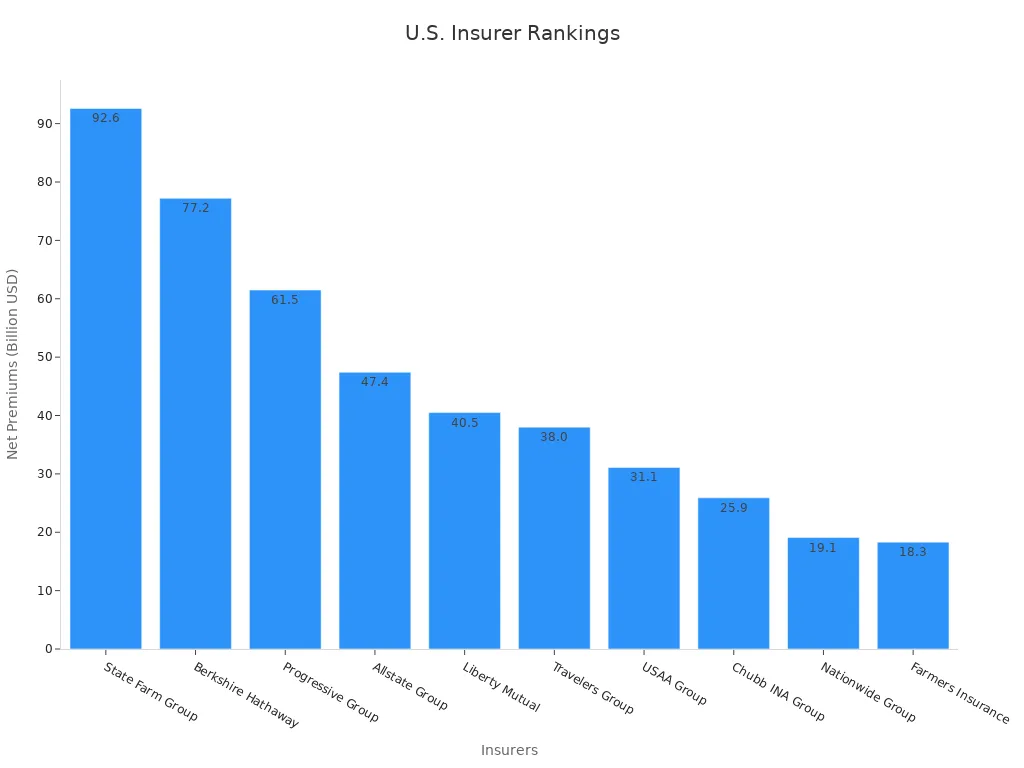
Banks in the United States have seen changes in their rankings by life insurance asset portfolios. Over the past year, Bank of America has kept its lead, but Wells Fargo and JPMorgan Chase have moved closer in total life insurance assets. Some banks, like PNC Bank and Truist Bank, have increased their life insurance holdings. This shift shows that more banks now see life insurance as a key part of their business. Life insurance companies also face changes in their rankings. The table below shows the top insurers by net premiums written and their credit ratings. These numbers help explain why some banks and life insurance companies rise or fall in the rankings.
| Rank | Insurer | Net Premiums Written (USD) | Credit Rating (A.M. Best) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | State Farm Group | 92.6 billion | A++ (Superior) |
| 2 | Berkshire Hathaway | 77.2 billion | A+ (Excellent) |
| 3 | Progressive Group | 61.5 billion | A+ (Excellent) |
| 4 | Allstate Group | 47.4 billion | A+ (Excellent) |
| 5 | Liberty Mutual | 40.5 billion | A (Good) |
| 6 | Travelers Group | 38.0 billion | A (Good) |
| 7 | USAA Group | 31.1 billion | A (Good) |
| 8 | Chubb INA Group | 25.9 billion | A (Good) |
| 9 | Nationwide Group | 19.1 billion | A (Good) |
| 10 | Farmers Insurance | 18.3 billion | A (Good) |
Influencing Factors
Several factors drive changes in life insurance asset rankings among banks and life insurance companies. Rising interest rates have a big impact. When rates go up, policyholders may surrender their life insurance policies. This action forces life insurance companies to sell assets quickly, sometimes at a loss. Banks that manage life insurance assets must watch these risks closely. Liquidity risk and asset-liability management play a large role. Many life insurance companies use duration matching to reduce risk, but the share of illiquid assets keeps growing. This trend makes it harder for both banks and life insurance companies to stay stable during market stress.
Stress testing and regular risk checks help banks and life insurance companies prepare for sudden changes. These tests use real numbers to show how much risk each group faces. Banks that use strong asset-liability management can keep their life insurance portfolios steady. Life insurance companies with high credit ratings and large net premiums written often hold their top spots. The market size, measured by net premiums, and financial strength, shown by credit ratings, both affect rankings. As banks and life insurance companies adjust their strategies, the rankings will keep changing.
Note: Life insurance remains a vital asset for banks and life insurance companies. Market trends, risk management, and financial strength all shape the rankings seen today.
The largest banks in the United States lead in life insurance asset management by holding strong portfolios and using advanced strategies. Life insurance helps these banks manage risk, support growth, and provide steady returns. Recent research shows that life insurance companies keep cash liquidity just under 3%, which experts consider adequate. Banks and insurers now invest more in private credit and structured products, raising yields and expanding the market. Life insurance asset rankings give a clear view of financial strength and highlight how top banks use life insurance to stay ahead in a changing market.
FAQ
What is life insurance in banking?
Banks use life insurance as an asset. They buy policies on employees and use the cash value for income and stability. This helps banks manage risk and support growth.
Why do banks invest in life insurance?
Banks invest in life insurance because it offers steady returns. The cash value grows over time. This helps banks pay for employee benefits and meet capital requirements.
How does life insurance help bank stability?
Life insurance gives banks a reliable asset. The cash value supports the bank’s balance sheet. It also helps banks handle unexpected expenses and market changes.
What is bank-owned life insurance (BOLI)?
Bank-owned life insurance means a bank owns policies on employees. The bank receives the cash value and death benefits. This helps banks manage costs and improve financial strength.
How do banks and life insurance companies differ?
Banks use life insurance to support their main business and manage risk. Life insurance companies focus on selling policies and managing claims. Both groups use different strategies to grow.
Capitalize on opportunities in U.S. banks’ life insurance asset management with BiyaPay! Our multi-asset wallet offers fee-free USDT conversions to fiat currencies like USD, with only a 0.5% fee for overseas bank transfers, enabling direct trading of leading bank stocks like JPMorgan Chase. Sign up in just 1 minute to bypass complex overseas account setups and execute secure, real-time transactions.
Whether investing in bank-driven insurance products or diversifying with blue-chip stocks, BiyaPay ensures cost-efficiency and reliability. Take action now—visit BiyaPay to register and streamline your investment journey!
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.
Related Blogs of

How to Wire Transfer USD from Industrial and Commercial Bank of China to OCBC Singapore? This Guide is All You Need

Another Major Drop! Why Is the A-Share Index Falling Non-Stop – Where Exactly Is the Problem?

Want to Predict A-Share Market Moves? Understanding These 5 Macro Signals Is Enough

Stop Relying Only on the Shanghai Composite: How the Shenzhen Component and ChiNext Indices Reveal New A-Share Opportunities
Choose Country or Region to Read Local Blog
Contact Us
BIYA GLOBAL LLC is a licensed entity registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC No.: 802-127417); a certified member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (Central Registration Depository CRD No.: 325027); regulated by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
BIYA GLOBAL LLC is registered with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), an agency under the U.S. Department of the Treasury, as a Money Services Business (MSB), with registration number 31000218637349, and regulated by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
BIYA GLOBAL LIMITED is a registered Financial Service Provider (FSP) in New Zealand, with registration number FSP1007221, and is also a registered member of the Financial Services Complaints Limited (FSCL), an independent dispute resolution scheme in New Zealand.



















