- Remittance
- Exchange Rate
- Stock
- Events
- EasyCard
- More
- Download
Stock Split: NVIDIA's 10-for-1 Impact on Price
Stock splits used to be common in the stock market, but their frequency has decreased since 2000. When a company’s stock price rises too high, it can reduce trading volume and deter investors, especially retail investors, leading to less active trading. In such cases, companies may consider splitting their stock. Examples include large companies like Apple, Google, and Tesla, which have often used stock splits to lower their stock prices and attract more investors.
For instance, Apple Inc. has conducted several stock splits, with the most recent being a 4-for-1 split in 2020. This made Apple’s stock more affordable and attracted more retail investors. In the months following the split, Apple’s stock price continued to rise, driven not only by the split itself but also by increased confidence in Apple’s innovative products and strong financial performance.
Stock splits can make shares more attractive, especially to smaller investors. Lower share prices can increase market liquidity and activity, enhancing the stock’s tradability.

However, some high-performing companies, like Berkshire Hathaway (BRK.A), have never split their stock. Berkshire Hathaway’s stock price has exceeded $620,000 per share, limiting retail participation but reflecting long-term growth and market trust.
Recently, NVIDIA announced on May 23 (Beijing time) that it will split its stock at a ratio of 10-for-1. This announcement has sparked widespread discussion in various stock exchange communities. In the Tiger Community, some investors believe that NVIDIA’s stock could rise to $150 after the split, while others think the split is aimed at joining the Dow Jones Index for greater influence.
In the BiyaPay stock community, U.S. stock investors compare NVIDIA’s stock split to a hard fork in cryptocurrency. A hard fork refers to a major upgrade or change in a blockchain network, creating two independent chains and different cryptocurrencies. For instance, Bitcoin’s hard fork resulted in Bitcoin Cash. Although the operations are not identical, there are similar concepts and practices in the cryptocurrency market. Hence, investors in the BiyaPay stock community liken NVIDIA’s stock split to Bitcoin’s hard fork.
BiyaPay is a multi-asset investment platform where investors can trade U.S. stocks, Hong Kong stocks, Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital currencies, as well as foreign exchange.
NVIDIA’s stock split decision will take effect on June 10 at the market opening, aiming to expand the company’s investor base. So, what exactly is a stock split for ordinary investors?
- What is a stock split? A stock split increases the number of shares a company has while reducing the price per share, keeping the total market value unchanged. For example, a 10-for-1 stock split turns one share into ten, increasing the number of shares a shareholder holds by ten times, but reducing the price per share to one-tenth of the original. Stock splits are usually used to increase a stock’s liquidity and make it more attractive.
- Impact of the stock split on NVIDIA’s stock price Short-term impact:
- Psychological effect: A lower stock price post-split makes it easier for investors to buy. This often leads to increased demand, potentially driving up the stock price in the short term.
- Increased liquidity: More shares usually mean more trading volume, making the stock more liquid. This benefits small investors who can buy more shares at a lower price.
- Market reaction: Historically, stock splits are seen as a sign of confidence from the company, suggesting better future performance, which can push up the stock price.
Long-term impact:
- Fundamentals unchanged: While a stock split might boost the stock price in the short term, it doesn’t change the company’s fundamentals or market value. Long-term price trends depend on company performance and market conditions.
- Impact of the stock split on NVIDIA’s options Options contract adjustments:
- More contracts: The number of shares in each options contract will increase after the split. For example, a 10-for-1 split will increase the shares in each contract from 100 to 1,000.
- Adjusted strike price: The strike price will be adjusted according to the split ratio. If the strike price is $1,000, a 10-for-1 split will reduce it to $100.
- Unchanged total value: Although the number of contracts and strike prices change, the total value remains the same. For instance, before the split, one options contract represents 100 shares at a strike price of $1,000; after the split, it becomes ten contracts, each representing 100 shares at a strike price of $100, with the total value the same.
Increased liquidity and market impact:
- Increased liquidity: Like stocks, the trading volume of options usually increases after a split due to lower strike prices attracting more investors, enhancing liquidity.
- Investor behavior: Due to the transparent adjustments of options contracts, investors can quickly adapt to new terms, and market volatility may increase in the short term but typically normalizes quickly.
NVIDIA’s stock split will significantly impact its stock price and options market. In the short term, the stock price may rise due to increased liquidity and positive market sentiment. However, long-term price trends will still depend on company fundamentals and market conditions. The options market will adjust accordingly, ensuring that contract value remains unchanged and enhancing liquidity. Investors should closely monitor market changes post-split and make investment decisions based on new stock and options prices.
After introducing stock splits, let’s talk about reverse splits. A reverse stock split reduces the number of a company’s shares by combining multiple existing shares into one, increasing the price per share while keeping the total market value unchanged. For example, merging ten shares into one increases the price per share tenfold.
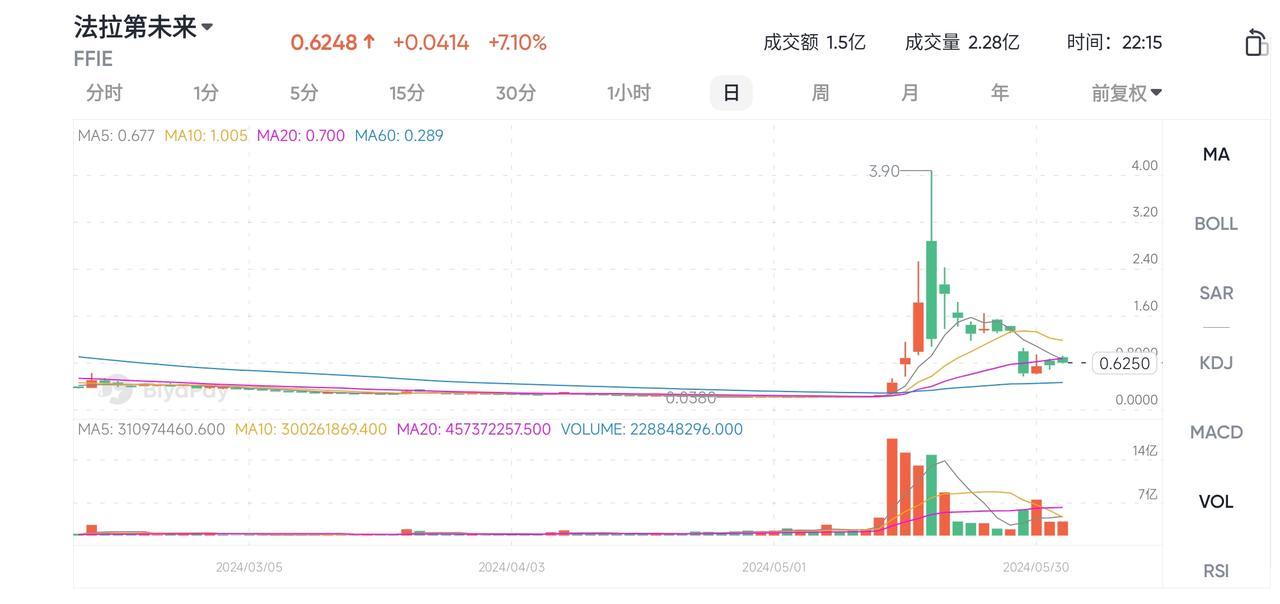
Reverse splits are used to raise low stock prices to meet minimum requirements for certain exchanges and avoid delisting. For example, Faraday Future has conducted multiple reverse splits to address low stock prices and maintain its NASDAQ listing. In 2022 and 2023, Faraday Future conducted 1:10 and 1:20 reverse splits, respectively.
These reverse splits immediately reduced the number of outstanding shares, increasing the trading price per share. For instance, after the 1:10 reverse split in 2022, the stock price rose from $0.50 to $5.00, and after the 1:20 reverse split in 2023, the price increased from $0.25 to $5.00. However, this did not save the company’s stock price and instead created a negative market impression, leading to a lack of investor confidence and a continuous decline in the stock price.
In 2024, Faraday Future was again on the verge of delisting. To avoid this, Jia Yueting launched a campaign to defend the stock price. Within half a month in May, Faraday Future’s stock rose from a low of $0.038 to a high of $3.9, an increase of over 100 times, demonstrating Jia Yueting’s determination.
Reverse splits have the following impacts on stock prices and options: Impact on stock prices:
- Stock price increase: The reduced number of shares increases the price per share. For example, a 1:10 reverse split raises a $10 stock price to $100.
- Market psychological impact: Reverse splits signal a company’s intention to raise its stock price, avoid delisting, or change its market image, which may temporarily boost investor confidence. However, long-term effects depend on the company’s fundamentals.
Impact on options:
- Adjusted strike prices: The strike prices of options will be adjusted according to the reverse split ratio. For example, a 1:10 reverse split multiplies the strike price by 10.
- Adjusted contract units: The number of shares in each options contract will be adjusted to maintain the total value. For example, a 1:10 reverse split reduces the shares in each contract from 100 to 10.
- Market value of options: The increase in the underlying stock price affects the intrinsic and time value of options, but the total value remains unchanged.
Reverse splits do not change a company’s total market value but adjust stock prices and options contracts’ specific parameters. Investors should monitor the company’s fundamentals and the market’s reaction to reverse splits.
Stock splits and reverse splits are tools used by company management to adjust stock prices, increase market liquidity, or meet exchange requirements. While stock splits are generally positive signals that attract more investors and boost stock prices, reverse splits may indicate financial challenges and should be approached cautiously. Investors should make informed decisions based on market reactions and company fundamentals to ensure the safety and profitability of their investments.