- Remittance
- Exchange Rate
- Stock
- Events
- EasyCard
- More
- Download
- Creator

Intel's Pain in Restructuring! With Increasing Losses, Is There Still a Chance for Its Stock Price t
Recently, Intel (NASDAQ: INTC) released its third-quarter financial report, which was less than satisfactory and showed that the company is still facing challenges on the road to restructuring. This veteran chipmaker is struggling to adjust its business to adapt to the rapidly changing technology market, yet its efforts don’t seem to have fully borne fruit. Nevertheless, the market’s reaction to this news has been relatively calm, indicating that investors still have expectations for Intel’s future performance.
It’s worth noting that the continuous losses in Intel’s foundry business have become a major pain point in the financial report. Some analysts believe that selling this business might be the best option for the company to focus on its core profitable areas. Meanwhile, although Intel’s stock price has experienced fluctuations, it is still considered attractive at present, with a relatively ideal balance between risks and returns.
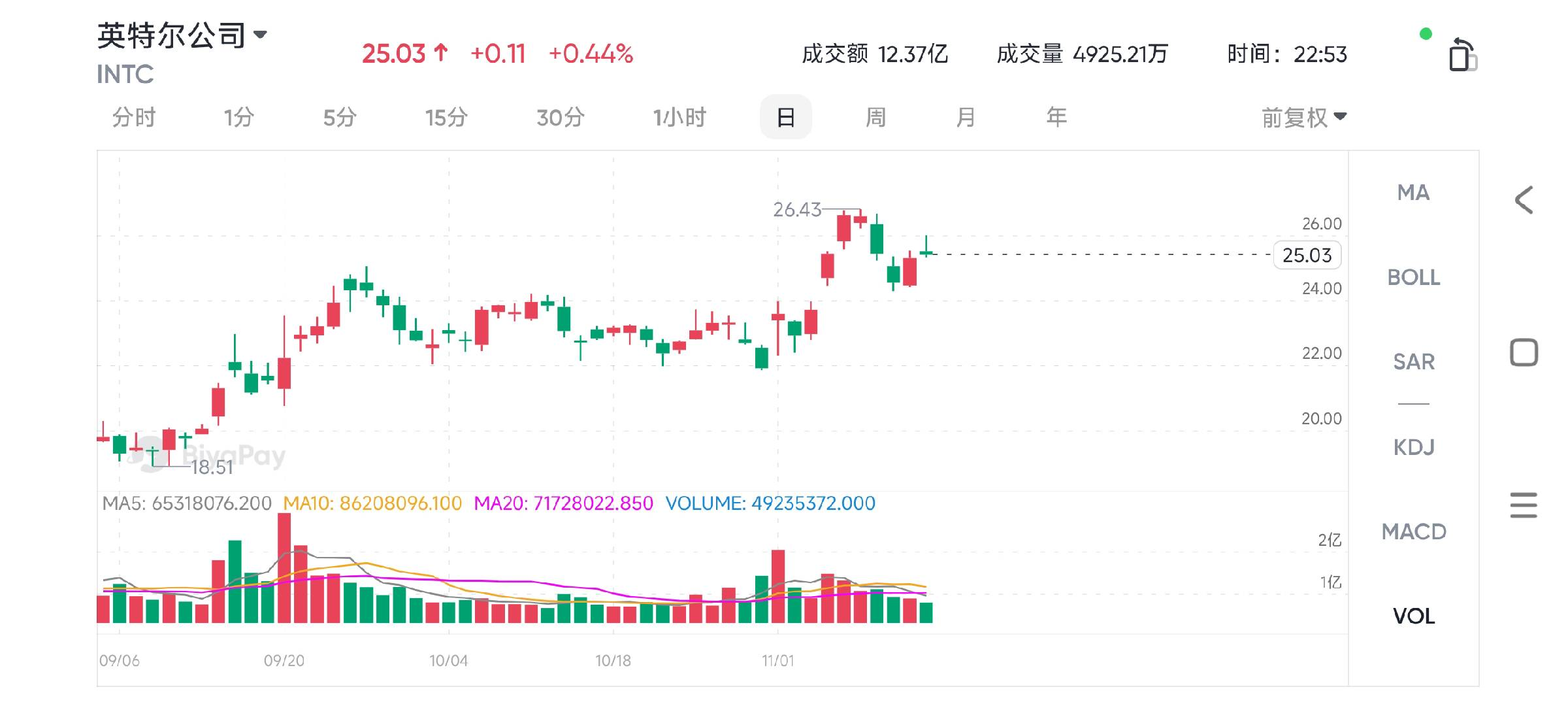
In recent weeks, the upward trend of Intel’s stock has shown the market’s optimism, and there may even be a short-term opportunity for the price to rebound technically. As the company gradually stabilizes during the restructuring process, we will continue to observe whether it can achieve the expected growth transformation in the future.
Market Opportunities: From AI to Data Centers
To seize the trend of the huge demand for high-performance computing chips brought by artificial intelligence, Intel has launched its latest AI accelerator, Gaudi 3. This product focuses on the training of deep learning models and can provide relatively lower costs while maintaining high performance. Through cooperation with the corporate giant IBM, Intel hopes to turn Gaudi 3 into an important solution in the AI field and win a place in the enterprise-level market.
Intel also foresees the potential of AI technology in the general consumer market, especially the growth of AI PCs.
The company predicts that by 2025, the shipment volume of AI PCs will reach 100 million units, demonstrating the broad prospects of AI hardware in daily computing. With this product line, Intel hopes to bring a new generation of intelligent experiences to the consumer market and regain growth momentum in the client computing market.
Growth in Data Center Demand
The data center market, as the pillar of the global digital economy, has developed at a faster pace than many expected.
Intel’s data shows that in the third quarter of 2024, its Data Center and AI Group achieved a 9% year-on-year growth, becoming a highlight in the company’s financial performance. To gain an edge in this highly competitive field, Intel has launched the Gaudi 3 AI accelerator designed specifically for data centers and cooperated with cloud service providers such as AWS to provide more efficient AI training solutions for data center customers.
In the next few years, the steady growth of the data center business is expected to bring continuous revenue support for Intel.
Expansion Opportunities for Foundry Services
Although Intel’s foundry services business is still in a loss-making state, the company is confident in the potential value of this area. In the third quarter of 2024 alone, the operating loss of this business reached $580 million, with a negative profit margin exceeding 134%. However, Intel plans to split the foundry business into an independent subsidiary to enhance its attractiveness and attract more third-party customers.
Recently, Intel reached a long-term cooperation agreement with AWS to produce customized AI chips and processors for it. This not only provides a stable revenue source for the foundry services but also shows that Intel is competitive in manufacturing services and can provide customized solutions for diverse customer needs.
Pain in Restructuring, Declining Profits
Intel’s financial performance in the third quarter showed the huge pressure the company is facing during the restructuring process. The quarterly data revealed a loss of $0.46 per share, while the market expected a profit of $0.02 per share. This is the second consecutive quarter that Intel’s profit has fallen short of expectations, reflecting the uncertainties and challenges during the company’s restructuring process.
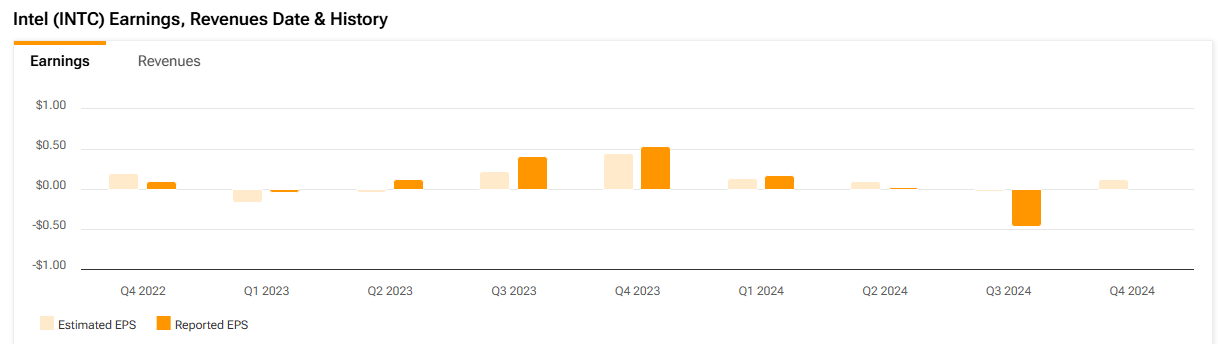
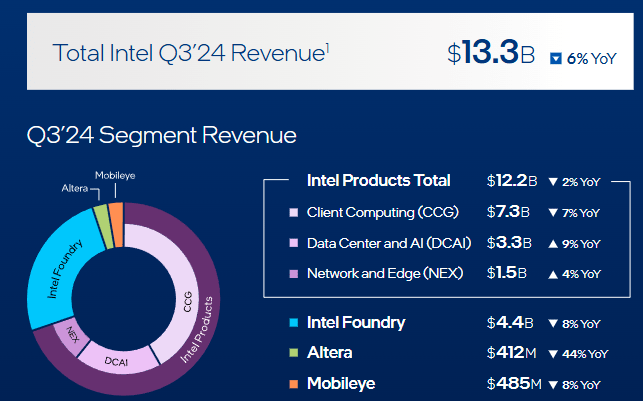
The company’s total sales in this quarter were $13.3 billion, a 6% year-on-year decrease. Although the revenue declined, it was in line with the sales forecast range of $12.5 billion to $13.5 billion given in the previous quarter, indicating that the decline in sales basically met market expectations. In the second quarter of 2024, Intel’s sales decreased by 1% year-on-year, mainly due to the weak performance of the Data Center, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Network & Edge Computing segments.
However, in the third quarter, these businesses gradually regained vitality. Among them, the Data Center and AI Group achieved a 9% year-on-year growth, and the Network & Edge Computing segment achieved a 4% year-on-year growth.
Meanwhile, the Client Computing Group, which produces desktop and laptop processors, performed poorly, with its revenue declining by 7% year-on-year, reflecting the sluggish demand in the overall PC market.
Nevertheless, Intel has high hopes for its emerging AI PC category and hopes that this product line can become a new growth engine in the future. The company predicts that by the end of 2025, the shipment volume of AI PCs is expected to reach 100 million units. If this goal is achieved, it will help promote the recovery of the client computing business.
From a profitability perspective, Intel’s core “Intel Products” segment (including Client Computing, Data Center and AI, Network and Edge Computing) has shown relatively strong profitability.
In this quarter, the total revenue of these core businesses reached $12.2 billion, a year-on-year decrease of only 2%. Among these businesses, the Client Computing Group is particularly prominent, achieving an operating profit of $2.7 billion in the third quarter and continuing to play an important role in the overall business structure.
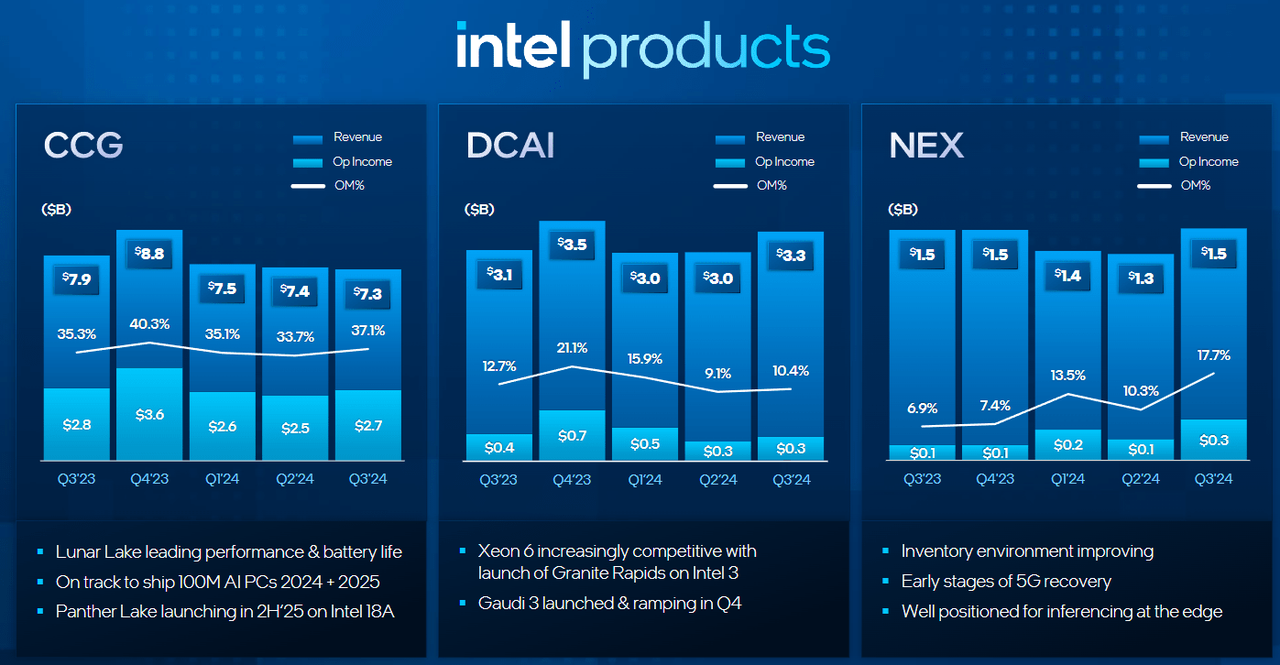
However, Intel’s foundry business remains the “pain point” of the company.
In the third quarter of 2024, the operating loss of this business was as high as $5.8 billion, with a negative profit margin reaching an astonishing 134.3%. Such a high negative profit margin means that the foundry business not only fails to bring any profits but also generates huge losses on the basis of revenue. In comparison, the loss of the foundry business in the previous quarter was $2.8 billion, with a negative profit margin of 65.5%, indicating that the financial situation of the foundry business has further deteriorated.
Faced with this situation of continuous losses, some market analysts believe that Intel may need to consider divesting the foundry business and focusing on the core areas of chip design and sales to relieve financial pressure. By focusing on more profitable businesses, Intel may be able to improve its overall operating efficiency and lay a more solid foundation for future sustainable development.
Valuation Analysis: Is Intel Still Undervalued?
Since the beginning of this year, Intel’s shareholders have experienced a significant shrinkage in market value, especially after the company announced its second-quarter financial report, when its stock price suffered a sharp decline. However, since September, Intel’s stock price performance has gradually warmed up, showing the market’s optimistic expectations for its future prospects. At present, the stock price has regained the important short-term indicator of the 50-day moving average, suggesting that the market may think that Intel’s trough has passed.
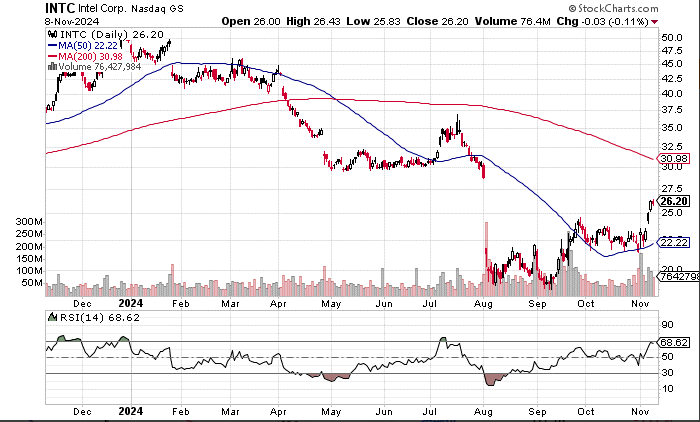
If the company can successfully promote the restructuring, the stock price is expected to rebound to $29, thus filling the previous gap, which will also bring a stronger bullish signal for Intel’s stock prospects.
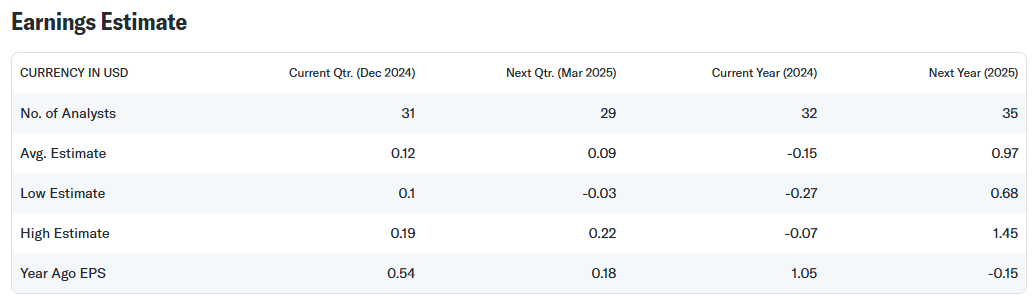
From a valuation perspective, Intel’s current pricing level appears relatively cheap in the industry, especially considering the company’s potential future earnings growth space. Although the company may record a loss of $0.15 per share in 2024, the market expects that the earnings per share will rebound to $0.97 in 2025.
If the restructuring plan is successfully implemented, Intel’s profitability is expected to be significantly improved.
Calculated at the current stock price of about $26, the price-earnings ratio is about 27 times, slightly lower than that of its competitor AMD, which is 29 times. With new products such as the AI accelerator Gaudi 3 gradually opening up the market, Intel’s future revenue structure is expected to be more diversified, which will further enhance the company’s competitiveness in the AI and data center fields and bring new growth drivers for the company’s market value.
Looking ahead, Intel’s restructuring progress and product innovation will directly affect the magnitude of its valuation rebound. It is expected that by 2026, as the restructuring nears completion, the company will gradually restore stable earnings growth, especially when the layout in the AI and data center fields is gradually realized.
For investors, Intel’s current valuation level may provide an attractive entry point. For those who want to enter the market early, it is recommended to use the multi-asset wallet BiyaPay to buy this asset as soon as possible. The current price indicates that investors still have the opportunity to enter at a low price. Moreover, BiyaPay supports trading in US and Hong Kong stocks as well as digital currencies, facilitating users to regularly check price trends and quickly complete deposit and withdrawal operations at critical moments.
If you encounter problems with fund deposits and withdrawals, BiyaPay provides efficient, safe, and unfrozen card solutions. Whether it is recharging digital currencies and converting them into US dollars or Hong Kong dollars, or withdrawing funds to a bank account, it can quickly and flexibly meet the fund needs and ensure that investors do not miss any market opportunities.
Risks Still Exist, Caution in Investment
The investment prospects of Intel are full of complexity. Although I am confident in its ultimate recovery and think it is worth buying at present, there are many factors that may weaken this view.
From the perspective of competition, this is a key issue. According to Argus Research’s data, Intel’s market share in the client and data center CPU markets has been on a downward trend for 18 consecutive years. Competitors such as AMD and ARM have adopted a series of aggressive strategies and dominated the market with new and optimized products, which is an important reason for Intel’s market shrinkage.
Although Intel has ambitious plans such as the 18A and Panther Lake processors, for these plans to have a positive impact on Intel’s market share, its products must make substantial progress in terms of performance and customer acceptance. Otherwise, once the product delivery fails or is delayed, Intel’s recovery strategy will be impacted.
In addition, the risk of investing in Intel also lies in the possible deviation of the current market consensus. Some major bank research reports show that some analysts are not optimistic about Intel and even rate it as “sell”, and Goldman Sachs’ latest report is an example.
Meanwhile, Intel is currently in a difficult restructuring stage, and investors should not be overly optimistic in the short term. In my opinion, the best way for Intel to get out of the predicament is to consider divesting the foundry business, because the foundry business is currently the biggest drag on Intel’s profit growth. In terms of operating profit growth, it is expected that the foundry business (Foundry) will continue to hinder Intel’s growth pace.
However, the prospects of Intel’s products are not completely bleak, especially as the sales of Gaudi 3 began to expand in the fourth quarter of 2024, and the situation may improve.
For investors, if they are optimistic about Intel’s long-term prospects in the AI and data center markets, they can regard it as a potential growth opportunity. However, since the company’s restructuring is still in a transitional period and may face relatively large market fluctuations in the short term, it is recommended that investors adopt a medium- to long-term holding strategy and adjust their investment portfolios in a timely manner according to market changes and restructuring progress. If the company can promote the restructuring and achieve technological breakthroughs as scheduled, Intel’s stock price is expected to rebound to a reasonable valuation level, bringing considerable returns to investors.