- Remittance
- Exchange Rate
- Stock
- Events
- EasyCard
- More
- Download
Intel Attempts Strategic Transformation: Selling Chip Manufacturing Business to Save the Day? Is it
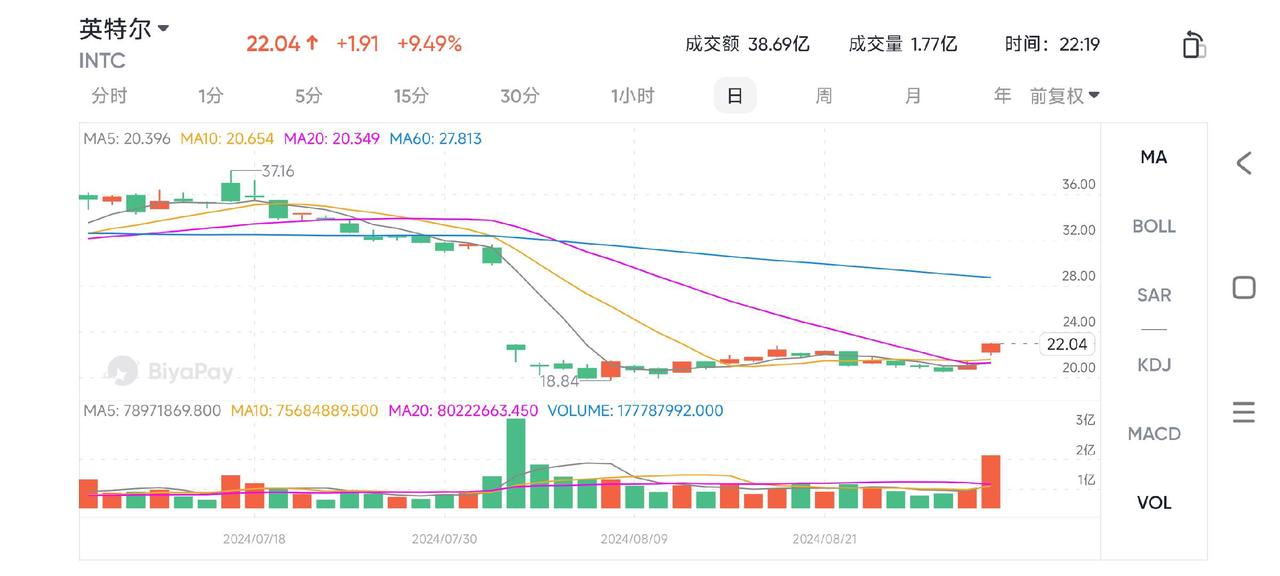
In today’s rapidly changing global technology landscape, each strategic adjustment by semiconductor giant Intel (Intel) impacts market nerves. Recently, Intel’s stock price surged by 9%, drawing widespread attention from investors and analysts. This surge may be attributed to rumors that Intel plans a major overhaul of its foundry business—selling or spinning off its chip manufacturing operations. Such a potential decision not only marks a significant shift in Intel’s strategic direction but could also profoundly affect its competitive edge in the semiconductor industry.

Intel’s Current Predicament and Challenges
Intel, a behemoth in the global semiconductor industry, faces unprecedented challenges that affect not only its market position but also its stock price. Here are the main challenges currently faced by Intel:
Decline in Financial Performance
Intel’s recent financial reports reveal weak performance. In Q2 2024, the company’s revenue fell by 1% year-over-year, and net profits turned to a loss of $1.6 billion. This downturn triggered market concerns about Intel’s future profitability, leading to a significant stock price decline. Investors are questioning whether the company can maintain its historical profit levels and growth trajectory.
Fierce Market Competition
In the competitive landscape of the semiconductor industry, Intel faces intense competition from AMD, NVIDIA, and TSMC. These competitors’ proactive performances in technology innovation and market strategy have caused Intel to lose market share in key areas, such as data centers and AI chip markets.
Particularly in high-performance computing and graphics processing, Intel’s products face stiff competition, adding pressure on its revenue and profit margins and exacerbating financial strains.
Technological Development Lag
Intel appears to be lagging in the technology development race. The company’s progress in developing advanced process technologies, especially in transitioning to smaller nanometer processes, places it at a disadvantage compared to competitors who adopt more advanced processes.
The market is concerned about Intel’s ability to timely launch competitive new products, affecting investor confidence in the company’s future growth potential and putting pressure on the stock price.
Urgency in Cost Control and Strategic Adjustments
Facing financial pressures and market competition, Intel has had to implement several cost-cutting measures, including a 15% workforce reduction, dividend suspension, and capital expenditure control. While these measures aim to improve the company’s financial health in the short term, they could negatively affect long-term development and employee morale. Meanwhile, the company is considering divesting its chip manufacturing business, adding uncertainty to Intel’s future direction.
In the backdrop of declining financial performance, intensified market competition, lagging technological development, and urgent cost control and strategic adjustments, Intel is exploring a series of strategic transformation measures to reclaim its leadership in the semiconductor industry. Rumors suggest significant adjustments to its foundry business, including selling or spinning off its chip manufacturing operations.
These rumored strategic moves undoubtedly add uncertainty to Intel’s future but could also bring new vitality to the company.
Intel’s Foundry Business Possibly for Sale
Intel’s foundry business, Intel Foundry Services (IFS), was once a strategic ace, embodying the company’s ambition to expand in semiconductor manufacturing.
However, as the global chip market competition evolves and internal financial pressures increase, Intel must reassess this strategy. Recent rumors about the potential sale of this business have sparked widespread industry interest.
According to the latest financial report, in Q2, Intel’s adjusted earnings per share were $0.02, below the expected $0.08 and last year’s $0.13. The major misstep was revenue falling short of expectations at $12.8 billion, a 1% year-over-year decline, primarily due to a weak traditional data center CPU market as the industry shifts spending toward AI chips. This indicates that Intel’s financial condition is challenging, and the potential sale of the foundry business could be one of the measures to improve financial conditions and refocus on core operations.

Despite Intel’s considerable capabilities in chip design and manufacturing technology, its foundry business has not performed financially as expected. With competitors like TSMC and Samsung making rapid advancements in advanced process technologies, Intel’s deficiencies in cost control and market response have become apparent, affecting the foundry business’s profitability and attractiveness to potential clients.
In competition with these rivals, the market value and strategic position of Intel’s foundry business are being challenged. TSMC’s leadership in advanced process technology and efficient production capacity has made it the frontrunner in the global chip foundry market, with Samsung closely following through aggressive investments and strategies.
Facing such competitive conditions, Intel’s foundry business seems to be struggling in terms of technology and cost.
Potential Risks
Considering the sale of its foundry business can be seen as a strategic refocusing for Intel.
By divesting this part of its business, Intel can concentrate more resources and energy on its core operations, such as client computing and data center markets, which remain the main sources of revenue and profit. This also helps Intel alleviate financial burdens and improve its overall financial condition.
However, selling the foundry business could also pose potential risks. Losing control over key manufacturing capabilities might affect Intel’s ability to innovate in certain technology areas, especially in emerging markets like artificial intelligence and autonomous driving.
These markets have a growing demand for high-performance semiconductors, and Intel’s long-term competitiveness in these areas could be impacted.
Market Expectations and Reactions
At this critical juncture, Intel’s strategic focus is shifting, with the company increasing investments in areas like artificial intelligence, autonomous driving, and 5G technology to secure a favorable position in these rapidly growing markets. Through collaborations with industry leaders and optimal resource allocation, Intel aims to maintain a leadership position in future technology innovations.
The potential sale of Intel’s foundry business has a complex and multifaceted impact on the stock price.
On one hand, the market might interpret this move as a positive signal that the company is alleviating financial burdens and focusing on core businesses, which could boost the stock price in the short term.
On the other hand, if the market perceives the sale as Intel abandoning a significant position in semiconductor manufacturing, it might raise doubts about the company’s long-term growth prospects and market position, potentially negatively affecting the stock price.
Ultimately, Intel’s stock price will depend on how the market interprets this strategic decision and the company’s performance after implementing it.
Is Now the Time to Buy the Dip?
From an investor’s perspective, the significant pullback in stock price might offer an attractive entry point, but whether it is truly a good time to buy the dip requires a deeper analysis of Intel’s fundamentals and market prospects.
Initially, Intel’s foundry business (IFS) incurred a $7 billion operational loss in 2023, with sales totaling $18.9 billion, a 31% year-over-year decline, which undoubtedly raises concerns. However, Intel’s Q2 2024 financial report showed some positive signals, such as exceeding expectations in client computing group (CCG) revenue and robust performance in the data center and artificial intelligence (DCAI) division.
These highlights indicate that despite facing challenges, Intel’s core business remains competitive, so interested friends can monitor market trends on multi-asset wallets like BiyaPay and wait for the right time to buy.
If there are difficulties with deposits and withdrawals, consider using it as a professional US and Hong Kong stock deposit and withdrawal tool, converting cryptocurrencies into USD or HKD, withdrawing to a bank account, and then depositing into other brokerages to buy stocks, with fast transaction speeds, unlimited amounts, and no delays in market trends.

Intel’s IDM 2.0 Strategy
Intel’s IDM 2.0 strategy and its investment plans in Arizona and Ohio demonstrate the company’s commitment to enhancing its manufacturing capabilities and competitiveness. Intel aims to launch 20A node products by 2024 and regain a leading position by 2025, showing a clear technological development blueprint and ambitions for future growth.
However, potential risks should not be overlooked, including intense market competition and the execution risk of internal restructuring.
In summary, while Intel’s stock price may face challenges from these factors in the short term, the company’s innovation capabilities and market position could provide new growth opportunities in the long term.
Intel’s strategic adjustments, including the possible spin-off of its foundry business, aim to address financial challenges and reshape its market position. Although the market has reacted positively and the stock price has rebounded, this transformation comes with risks. Investors considering whether to buy the dip should weigh Intel’s core business strength, execution risks of the transformation strategy, and the global market competition landscape.
Intel’s future will ultimately depend on the successful execution of its strategy and its ability to adapt to market changes. Investors are advised to closely monitor the company’s strategic progress and industry trends to make prudent investment decisions.