- Remittance
- Exchange Rate
- Stock
- Events
- EasyCard
- More
- Download
The Complete Guide to ETF Investment: How to Master U.S. Stock ETFs?
ETFs are an incredibly practical tool for investing in U.S. stocks, yet many investors have a superficial understanding of them. Some view ETFs as a lesser version of mutual funds, others consider them too stable with slow profit gains, and some even think of ETFs as a strategy only for novice investors.
These misconceptions arise from a lack of familiarity with ETFs. In reality, ETFs are complex yet adaptable investment tools. They have a broad range of applications and extremely flexible operational methods. When used properly, ETFs can yield returns comparable to individual stock picking, but with significantly reduced investment risk and less effort required.
Today, let’s explore some investment strategies for ETFs, as well as opportunities for investing in them.
Basic ETF Strategies
Let’s start with the basic strategies for ETFs, which are highly suitable for beginner investors but are not limited to them.
The Risks of U.S. Stocks
For many newcomers to the stock market, the biggest challenge is not stock selection or timing, but a proper understanding of market risks—a point often overlooked. Think about it: What determines whether a newcomer can succeed in the stock market? While you might think it’s all about making money, it’s actually the risks involved in the stock market that are decisive. Beginner investors often have extreme reactions to risk: some are terrified and hesitant to invest, while others completely ignore risks in pursuit of gains. The result is either delayed investments, missing out on great opportunities, or reckless moves that lead to total losses. Therefore, a correct initial understanding of stock market risks is crucial for sustained success in investing. Investing in ETFs is an excellent method to help beginners grasp investment concepts and manage risks effectively. Moreover, investing is a long-term endeavor. If you approach the stock market with a long-term investment mindset, you are already ahead of many current players.
Systematic Investment as the Best Entry Method
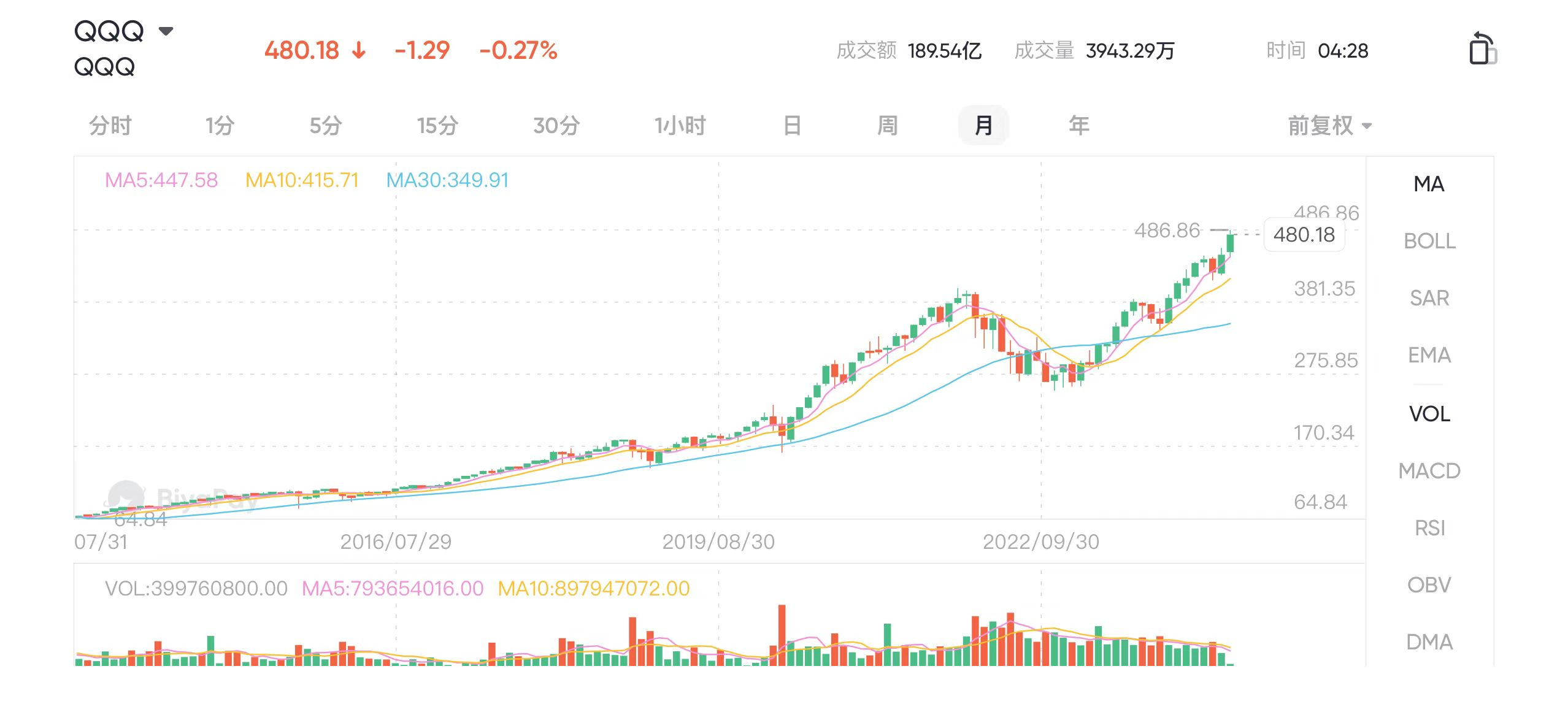
For beginner investors, the best entry strategy is systematic investment in major U.S. stock index funds, such as QQQ. These broad market index funds are the best ETFs for controlling individual stock risks. Systematic investment is also ideal for beginners and busy working professionals who do not have time to monitor the market constantly. However, which one is most suitable for you?
4
How to Choose the Right ETF for Yourself?
Choosing an ETF involves several steps. First, you need to be clear about the sector you want to invest in. For instance, if you are interested in renewable energy ETFs, start by identifying which ETFs are available in that sector. Then, compare several key pieces of information to select the best one.
Choose well-established management companies and renowned fund managers. I have seen too many small ETFs change their investment strategies without notice, and poorly managed ones that have closed are not uncommon. A critical indicator to look at is the Assets Under Management (AUM). If the AUM is less than $20 million, you might as well disregard that ETF.
Examine the top 10 holdings and their proportions. Generally, if you do not agree with the largest ten companies held by the ETF, then it may not be suitable for you. Likewise, if a company you highly value, such as Tesla in the renewable energy sector, is not included in the ETF or is only a minor part of it, then it may not be the right choice.
Consider management fees and dividends. Naturally, the lower the management fees, the better, and the higher the dividends, the better. By comparing a few similar funds, you can find the best option.
Once you choose the right ETF, you can start investing systematically on schedule. With basic ETF strategies, you do not need to make many market judgments or have an in-depth understanding of individual stocks. This period is meant for you to slowly grasp the market with the right mindset and develop your investment acumen. Remember, this is not easy; if you can manage it, you’re already doing better than many others.
How to Choose an ETF Trading Platform?
Since ETFs can be traded like stocks, you will need an investment account for U.S. stocks. Typically, choose a broker with a good reputation and a convenient platform for deposits and withdrawals. I usually use Interactive Brokers as my stockbroker, as it allows me to invest globally across almost all types of securities—stocks, bonds, commodities, futures, and various derivatives.

For deposits and withdrawals, I recommend using the multi-asset trading wallet BiyaPay. You can first deposit digital currencies like USDT into BiyaPay, then transfer USD via remittance to your Interactive Brokers bank account to invest in ETFs. A major advantage is that there is no limit to the amount you can transfer—millions of dollars can be processed quickly, with same-day remittance and arrival. Additionally, BiyaPay also allows direct trading of U.S. stocks and ETFs, making it very convenient for you to invest in the ETFs you prefer on this platform.
Advanced ETF Strategies
After you have mastered the basics of ETF investing in U.S. stocks and if you still possess an active investing spirit, you should have a reasonable understanding of the market and may have identified some stocks you favor. At this point, you are ready to engage in advanced ETF strategies.
The focus of advanced ETF strategies lies in asset allocation. Investment returns from stocks consist of three components: stock selection, timing, and asset allocation. While retail investors are most concerned with timing and stock selection, which indeed can provide higher short-term returns, asset allocation is the decisive factor for long-term investment returns. Studies show that timing contributes 2%, stock selection contributes 4%, and the remaining 94% of investment returns are driven by asset allocation. Therefore, for long-term investment success, proper asset allocation is crucial.
Core-Satellite Strategy
A method for optimizing asset allocation using ETFs is known as the core-satellite strategy. This strategy uses passive ETF investments as the core holdings, supplemented by multiple active investments as satellites. The purpose of the core-satellite strategy is to secure market-rate returns while seeking additional excess returns. Although the strategy seems straightforward, its principles and operational methods are quite sophisticated.
Advantages of the Core-Satellite Strategy
The core-satellite strategy offers three major advantages unmatched by other traditional investment methods:
- High Certainty: The core and satellites in this strategy represent the two most mainstream investment approaches in the market—long-term holding for the core and active management for the satellites. These strategies complement each other during different market conditions, allowing at least one strategy to have an advantage, thereby reducing risk while capturing investment opportunities.
- Flexibility: Investors can adjust parts of their satellite investments to achieve alpha, or excess returns, without the need to overhaul the entire portfolio. The core strategy also ensures a significant part of the beta, or the overall market returns, providing flexibility while minimizing exposure to excessive risk.
- Personalization: Just as no two leaves are identical, no two investors are the same. Pure ETF investments might not meet the specific needs of every investor. The core-satellite strategy allows you to adjust your core holdings and their proportions based on your risk preference, investment duration, and amount.
How to Operate the Core-Satellite Strategy?
Let’s look at how to implement the core-satellite strategy:
- Choosing Core Investments: The choice of core investments is crucial since most of the returns come from this segment. The best approach is to select from the major U.S. indices, such as the S&P 500 index fund (SPY), NASDAQ index fund (QQQ), and Dow Jones index fund (DIA). These funds not only offer excellent diversification, but their options also provide liquidity and flexibility to investors.
- Selecting Satellites: This step tests your investment acumen and is key to achieving alpha. Your choice of satellites will vary by individual, but it is important to ensure that the satellites are not too closely correlated with the core. For example, if you use a tech-heavy QQQ as your core and also allocate satellites heavily in tech stocks, you might face synchronized gains and losses. Instead, you could switch the core to SPY or diversify satellites across different sectors to better withstand risks, like tech stock downturns.
- ETFs as Satellites: Choosing ETFs for your satellites, such as sector or strategy-specific ETFs, can be effective, especially for investors who do not have time to monitor the markets constantly. This method also allows you to position yourself ahead of major sector rotations and find investment opportunities gradually.
- Balancing Core and Satellite Proportions: There is no one-size-fits-all answer for the right balance between core and satellite investments. You need to adjust this ratio based on your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and amount. Younger investors might afford more risk, opting for a smaller core proportion with riskier ETFs like QQQ. As you age and your assets grow, you might reduce risk by increasing the proportion of core investments and selecting safer options.
Conclusion
Unlike basic strategies that require minimal market judgment, advanced strategies like these require an ability to assess market trends and an understanding of specific stocks or sectors. After this discussion, you should be able to find an ETF investment strategy that fits your needs perfectly.